Content Menu
● What is a Movable Scaffolding System (MSS)?
● Types of Movable Scaffolding Systems
>> Modular Design for Versatility
>> Case Example: Bridge Over Water
● Applications of Movable Scaffolding Systems
● Limitations and Considerations
● Design Innovations in Movable Scaffolding Systems
● Real-World Success Stories
>> Urban Highway Expansion
>> Mountain Bridge Project
● Summary
● FAQ
>> 1. What is a Movable Scaffolding System and how does it differ from traditional scaffolding?
>> 2. Can an MSS be adapted for non-bridge projects?
>> 3. How does customization impact the cost and timeline of a project?
>> 4. What are the safety features of a customized MSS?
>> 5. How quickly can an MSS be reconfigured or moved to a new span?
Movable Scaffolding Systems (MSS) have fundamentally changed the landscape of modern construction, especially in bridge building and large-scale infrastructure projects. Their adaptability, modularity, and efficiency make them a top choice for engineers and contractors worldwide. But does this flexibility extend far enough to allow a movable scaffolding system to be customized for any project? This article explores the full potential of MSS customization, delving into their design, innovations, maintenance, future trends, and real-world applications.
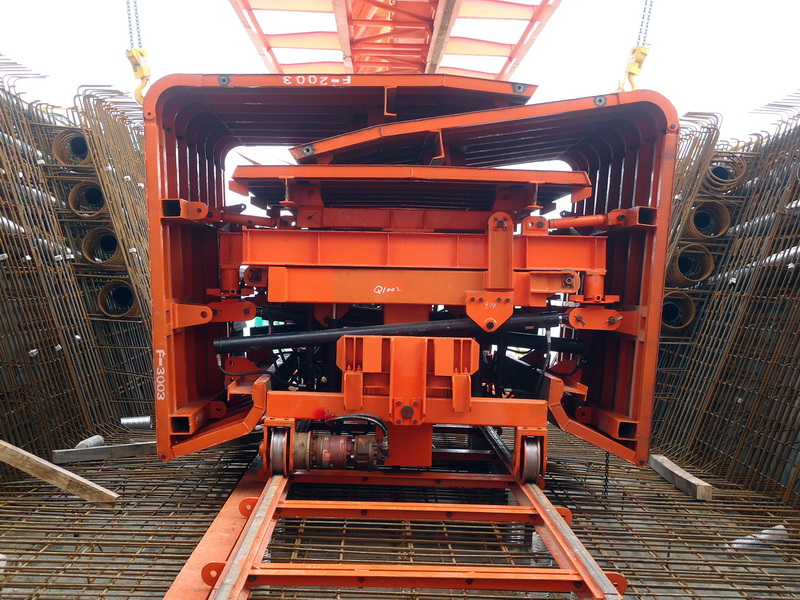

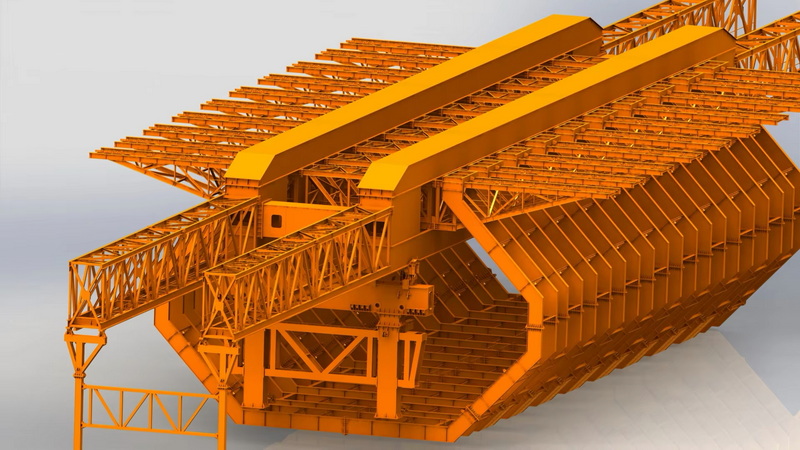
What is a Movable Scaffolding System (MSS)?
A movable scaffolding system is a specialized, self-launching structure mainly used for casting concrete bridge spans or segments in place. Unlike launching gantries, which handle precast segments, MSS supports the formwork as concrete is poured and cured, then moves to the next segment for repeated use.
- Efficiency: Enables span-by-span construction, allowing for rapid progress without disrupting ground-level activities.
- Safety: Provides stable access and support for workers at height, reducing risks.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reusable and adaptable, reducing material and labor costs over multiple projects.
- Minimal Environmental Impact: Especially useful where ground disturbance must be minimized, such as over water or protected terrain.
Types of Movable Scaffolding Systems
| Type | Description | Typical Use Cases |
| Overhead MSS | Forms suspended from girders above the deck level | High bridges, deep valleys |
| Underslung MSS | Forms supported by girders below the deck level | Lower bridges, urban areas |
| Self-Launching | MSS can relocate itself to the next span without cranes | Remote or hard-to-access sites |
Modular Design for Versatility
Modern MSS are designed with modularity at their core. This means components can be interchanged, adjusted, or extended to fit the unique geometry and requirements of each project. For example:
- Adjustable Main Supports: Tailored to the geometry of bridge columns or piers for optimal load transfer and stability.
- Custom Formwork: Adapted for different deck profiles, whether box, T-beam, or variable thickness.
- Span Length Flexibility: Engineered to handle spans up to 80 meters or more, accommodating both constant and variable depths.
Leading MSS manufacturers and engineering teams work closely with clients to design systems that meet the precise needs of each project, including:
- Site Constraints: Adapting to limited access, high piers, or water crossings.
- Environmental Factors: Weather-resistant materials and configurations for adverse conditions.
- Operational Requirements: Self-launching mechanisms for projects without crane access.
Case Example: Bridge Over Water
A bridge project over a wide river required an MSS that could span long distances and operate without ground support. The system was custom-engineered with extended girders, self-launching capability, and adjustable supports to match varying pier heights, demonstrating the adaptability of MSS to unique project challenges.
Applications of Movable Scaffolding Systems
| Application Area | Customization Examples | Benefits |
| Highway Bridges | Variable span lengths, parapet formwork | Fast, safe, minimal traffic disruption |
| Railway Bridges | Adaptable heights, under-track access | Maintains train operations during works |
| Industrial Projects | Custom shapes, confined space solutions | Supports complex formwork requirements |
| Power Plants | High-altitude, weather-resistant designs | Facilitates maintenance and upgrades |
| Maritime Structures | Adjustable for tidal variations, corrosion-resistant | Enables offshore and port construction |
- Reduced Downtime: Quick assembly, disassembly, and relocation minimize project delays.
- Enhanced Safety: Custom guardrails, platforms, and access points improve worker protection.
- Resource Efficiency: Reusable components and adaptable designs lower material waste and costs.
- Sustainability: Less environmental impact due to minimized ground disturbance and optimized logistics.

Limitations and Considerations
While MSS are highly customizable, certain factors must be considered:
- Initial Engineering: Custom solutions require detailed planning and engineering, potentially increasing upfront costs.
- Project Scale: MSS are most economical for large-scale, repetitive span projects; smaller or irregular projects may benefit more from alternative scaffolding solutions.
- Specialized Operation: Requires trained personnel for assembly, operation, and maintenance.
Design Innovations in Movable Scaffolding Systems
The field of movable scaffolding systems has seen significant design innovations in recent years, driven by the need for greater efficiency, safety, and adaptability.
Advanced Materials:
The integration of high-strength steel alloys and lightweight composites reduces the overall weight of MSS components, making them easier to transport and assemble while maintaining structural integrity.
Smart Technology and Automation:
Sensors embedded in the MSS monitor load distribution, structural health, and environmental conditions in real-time. This data allows engineers to make informed decisions, optimize system use, and enhance safety by detecting potential issues before they become critical.
Quick-Connect Modular Design:
Modern modular designs now include quick-connect mechanisms, reducing assembly time significantly. These allow for faster setup and breakdown, crucial for projects with tight schedules.
Regular maintenance and inspection are vital to ensure the safety and longevity of movable scaffolding systems.
- Routine Maintenance: Checking for wear and tear on mechanical parts, lubrication of moving components, and inspection of welds and joints for signs of fatigue or damage.
- Inspection Protocols: Visual checks and non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle inspection, help identify internal flaws not visible to the naked eye.
- Personnel Training: Proper training for assembly, operation, and maintenance teams is essential. Well-trained teams can identify potential problems early and perform maintenance tasks effectively, reducing accident risks and prolonging system service life.
The future of movable scaffolding systems is closely tied to advancements in construction technology and materials science.
- Robotics and Automation: Automated MSS could reduce the need for manual labor, increase precision, and improve safety during assembly and relocation.
- Sustainability: Future MSS designs are expected to use more eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient components, such as solar-powered sensors and actuators.
- Advanced Customization: Sophisticated software tools will enable engineers to design MSS tailored to highly complex and unique project requirements.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: These technologies may soon play a role in planning and training, allowing teams to simulate MSS operations before actual deployment.
Real-World Success Stories
Urban Highway Expansion
In a major city, an MSS was custom-designed to fit within a narrow urban corridor, allowing for the construction of new elevated lanes with minimal disruption to existing traffic. The system's modularity enabled rapid adaptation to varying span lengths and column placements.
Mountain Bridge Project
A high-altitude bridge required an MSS that could withstand extreme weather and operate on steep slopes. Engineers developed a hybrid MSS with reinforced weatherproofing and specialized anchoring systems, demonstrating the technology's adaptability even in the harshest environments.
Summary
Movable Scaffolding Systems can be extensively customized to meet the demands of virtually any large-scale construction project, particularly in bridge and infrastructure development. Their modularity, adaptability, and engineering flexibility allow them to overcome a wide range of site-specific challenges, from unique geometries to environmental constraints. As infrastructure needs grow and projects become more complex, the role of customizable MSS will only become more vital in delivering safe, efficient, and cost-effective solutions.
FAQ
1. What is a Movable Scaffolding System and how does it differ from traditional scaffolding?
A Movable Scaffolding System (MSS) is a modular, self-launching support structure used mainly for casting bridge spans in place. Unlike traditional scaffolding, which is stationary and assembled on-site, MSS can be moved along the project, supporting efficient, repetitive construction without affecting ground-level activities.
2. Can an MSS be adapted for non-bridge projects?
Yes, while MSS are most commonly used for bridges, they can be customized for industrial, power plant, maritime, and other large infrastructure projects that require large-scale, elevated formwork or access solutions.
3. How does customization impact the cost and timeline of a project?
Customizing an MSS can increase initial engineering and fabrication costs, but the overall project benefits from faster construction, reduced labor, and lower material waste, often resulting in net savings and shorter timelines for large projects.
4. What are the safety features of a customized MSS?
Custom MSS can include features such as adjustable guardrails, anti-slip platforms, secure access points, and weather-resistant materials, all designed to enhance worker safety and meet project-specific regulatory requirements.
5. How quickly can an MSS be reconfigured or moved to a new span?
Modern MSS are designed for rapid assembly, disassembly, and relocation. Self-launching systems can move to the next span in as little as a day, significantly reducing downtime between construction phases.






















