Content Menu
● Understanding System Scaffolding Components
● The Importance of Regular Maintenance and Inspection
● Developing a System Scaffolding Maintenance Schedule
● System Scaffolding Inspection Checklist
● Detailed Inspection Procedures
● Maintenance Best Practices
● Tools for Inspection and Maintenance
● Addressing Corrosion
● Training and Competency
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. How often should system scaffolding components be inspected?
>> 2. Who is responsible for inspecting system scaffolding?
>> 3. What are some common signs of damage to look for during an inspection?
>> 4. How can corrosion be prevented on system scaffolding components?
>> 5. What should be done with damaged system scaffolding components?
● Citations:
System scaffolding, known for its modularity and ease of assembly, is a popular choice in the construction industry. However, its safety and efficiency hinge on regular maintenance and thorough inspections of its components. Neglecting these aspects can lead to structural weaknesses, posing significant risks to workers. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to properly maintain and inspect system scaffolding components, ensuring a safe and productive work environment.

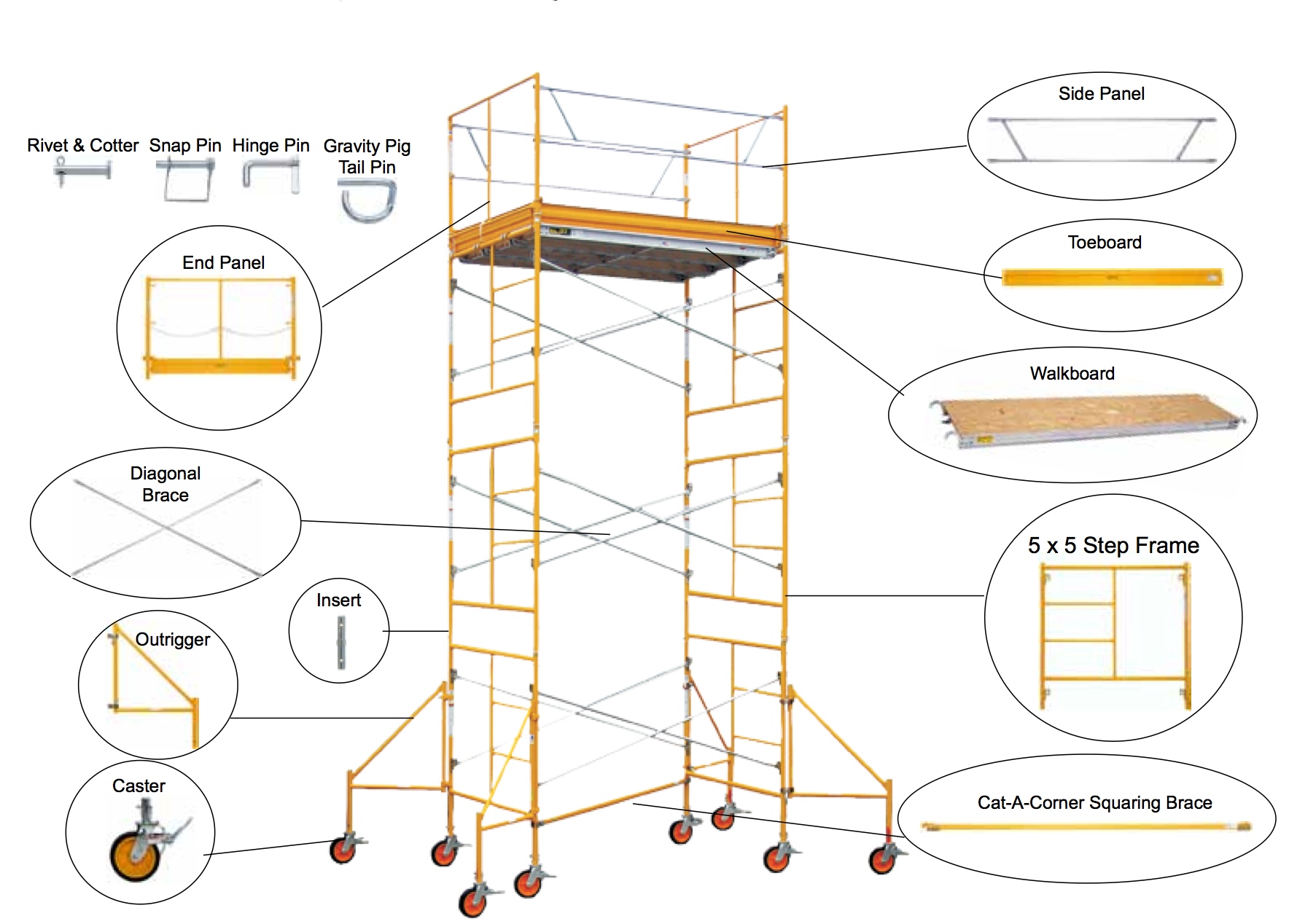
Understanding System Scaffolding Components
Before diving into maintenance and inspection, it's crucial to understand the core components of a system scaffolding setup. These typically include:
- Standards (Verticals): The main support posts of the scaffold.
- Ledgers (Horizontals): Horizontal members connecting the standards[1].
- Transoms: Shorter horizontal members providing additional platform support[1].
- Braces: Diagonal or horizontal members adding stability to the structure[3].
- Base Plates/Adjustable Legs: Used to level the scaffold and distribute weight[2].
- Couplers/Connectors: Devices used to join the components together.
- Platforms/Planks: The working surface of the scaffold[3].
- Guardrails: Vertical posts that act as a barrier to prevent falls[2].
- Toeboards: Vertical barriers at the edge of platforms to prevent tools and materials from falling[3].
The Importance of Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection are essential for several reasons:
- Safety: Identifying and addressing potential hazards before they lead to accidents[3].
- Compliance: Meeting regulatory requirements set by organizations like OSHA and local safety authorities [3, 6].
- Extended Lifespan: Proper care can significantly extend the lifespan of system scaffolding components[3].
- Cost Savings: Preventing damage and component failure reduces the need for costly repairs or replacements[3].
- Operational Efficiency: Well-maintained scaffolding ensures smooth and efficient workflow on the job site.
Developing a System Scaffolding Maintenance Schedule
A well-structured maintenance schedule is key to ensuring the long-term safety and reliability of system scaffolding. Here's how to develop one[3]:
1. Evaluate Scaffolding Needs: Consider factors like frequency of use, environmental exposure, and the types of loads the scaffolding will bear[3].
2. Research Industry Standards: Familiarize yourself with best practices and guidelines from OSHA and other relevant organizations[3].
3. Identify Maintenance Activities: Determine specific tasks needed, such as inspections, cleaning, repairs, and component replacements[3].
4. Set a Frequency: Establish how often each task should be performed based on usage, manufacturer recommendations, and regulatory requirements [3, 1].
5. Assign Responsibilities: Clearly define who is responsible for each maintenance task[3].
Here's an example of a system scaffolding maintenance schedule[3]:
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Responsible Party |
| Inspect components for damage | Before each use | Qualified worker |
| Clean scaffold surfaces | Monthly | Scaffold maintenance team |
| Replace worn or damaged components | As needed | Scaffold maintenance team |
| Perform load capacity tests | Annually | Qualified engineer |
System Scaffolding Inspection Checklist
A comprehensive inspection checklist is crucial for identifying potential problems with system scaffolding components. The following should be included in your checklist[3]:
- Foundation: Ensure the scaffold is built on a solid and stable surface[3].
- Structure: Examine for any signs of damage, such as bent or missing components, loose connections, or cracks[2].
- Stability: Verify the scaffold is level, plumb, and properly supported[2].
- Platform: Inspect the working platform for any deformations, breaks, or weak spots[2]. Ensure the platform is free from debris, tools, or any obstacles that may cause tripping hazards[3].
- Access Points: Check the access points[3].
- Bracing and Tie-ins: Ensure proper bracing and tie-ins[3].
- Guardrails and Toeboards: Ensure guardrails and toeboards are installed correctly and are in good condition[2].
- Load Capacity: Verify that the scaffold is not overloaded[3].
Detailed Inspection Procedures
The following are detailed inspection procedures for key system scaffolding components:
Standards (Verticals):
- Check for dents, bends, or corrosion [1, 3].
- Inspect the base plates for proper attachment and stability[2].
- Verify that the standards are plumb and properly spaced[2].
- Ledgers (Horizontals) and Transoms:
- Examine for bends, cracks, or corrosion [1, 3].
- Check the locking devices or connectors for proper function and secure attachment[2].
Braces:
- Inspect for bends, kinks, or damage to the connecting points[2].
- Ensure that braces are properly installed and tightened[2].
Platforms/Planks:
- Check for cracks, splits, or excessive wear [2, 3].
- Ensure that the planks are properly supported and overlap correctly[2].
- Verify that the platform is free from debris and slip hazards[3].
Couplers/Connectors:
- Inspect for damage, corrosion, or wear[2].
- Ensure that couplers are properly tightened and secured[2].
Maintenance Best Practices
In addition to regular inspections, the following maintenance practices will help prolong the life and ensure the safety of system scaffolding components[3]:
- Cleaning: Regularly clean scaffolding components to remove dirt, debris, and corrosive substances[3].
- Lubrication: Lubricate moving parts, such as connectors and locking devices, to ensure smooth operation[3].
- Repair: Promptly repair any damaged or worn components[3].
- Replacement: Replace components that are beyond repair or that do not meet safety standards[3].
- Proper Storage: Store scaffolding components in a dry, secure location when not in use. Protect them from harsh weather conditions and corrosive elements [3, 1].
Tools for Inspection and Maintenance
Having the right tools on hand makes inspection and maintenance tasks easier and more effective[5]:
- Level: To ensure that the scaffold is level and plumb.
- Tape Measure: For verifying dimensions and spacing.
- Wrench Set: For tightening and loosening couplers and connectors.
- Hammer: For tapping components into place.
- Wire Brush: For removing rust and corrosion.
- Lubricant: For lubricating moving parts.
- Inspection Checklist: A printed checklist to ensure all components are inspected.
- Camera: To document any damage or issues.
Addressing Corrosion
Corrosion is a major threat to scaffolding components, especially when stored or used in damp environments [1, 3].
- Protective Coatings: Apply protective coatings such as galvanizing or paint to prevent corrosion[3].
- Regular Cleaning: Regularly clean scaffolding to remove dirt and corrosive substances[3].
- Proper Storage: Store scaffolding in a dry, well-ventilated area [3, 1].
Training and Competency
-Ensure that workers using the scaffold are properly trained on its safe usage, maintenance, and inspection procedures-. Encourage a culture of safety and accountability among all employees[3].
- Competent Person: Daily inspections should be carried out by a competent person who has received training in scaffold safety[2].
- Qualified Inspector: A qualified inspector should inspect scaffold components for damage[3].
Conclusion
Proper maintenance and inspection of system scaffolding components are essential for ensuring a safe and productive work environment. By following the guidelines and procedures outlined in this article, construction professionals can minimize the risk of accidents, extend the lifespan of their equipment, and comply with safety regulations. Regular inspections, prompt repairs, and proper storage are all key components of an effective system scaffolding maintenance program.

FAQ
1. How often should system scaffolding components be inspected?
System scaffolding components should be visually inspected before each use and undergo a more thorough inspection weekly [2, 3].
2. Who is responsible for inspecting system scaffolding?
A competent person who has received training in scaffold safety should carry out daily inspections. A qualified inspector should inspect scaffold components for damage [2, 3].
3. What are some common signs of damage to look for during an inspection?
Common signs of damage include bent or missing components, loose connections, cracks, corrosion, and excessive wear [2, 3].
4. How can corrosion be prevented on system scaffolding components?
Corrosion can be prevented by applying protective coatings, regularly cleaning the scaffolding, and storing it in a dry, well-ventilated area[3].
5. What should be done with damaged system scaffolding components?
Damaged components should be promptly repaired or replaced with new components that meet safety standards[3].
Citations:
[1] https://www.safeworkaustralia.gov.au/system/files/documents/1703/guide-scaffold-inspection-maintenance.pdf
[2] https://www.unitedscaffold.ca/scaffold-news/best-practices-for-inspecting-scaffolding/
[3] https://scaffoldtype.com/scaffold-inspection-maintenance/
[4] https://ohsguide.ihsa.ca/en/topic/scaffolds_inspection
[5] https://mccausey.com/must-have-tools-for-scaffold-inspection/
[6] https://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/safety_haz/platforms/scaffolduse.html
[7] https://www.at-pac.com/how-to-perform-inspection-maintenance-on-scaffolding-parts-and-accessories-a-comprehensive-checklist
[8] https://www.nachi.org/commercial-scaffold-inspection.htm






















