Content Menu
● Understanding Mobile Tower Scaffolds
● What Defines a Mobile Tower Scaffold?
● Maximum Height Limits for Mobile Tower Scaffolds
>> International Standards and Regulations
>> Height-to-Base Width Ratio
>> Additional Height Limitations
● Factors Affecting Maximum Scaffold Height
>> 1. Base Dimensions and Stability
>> 2. Use of Outriggers and Tie-ins
>> 3. Load Capacity and Duty Rating
>> 4. Environmental Conditions
● Practical Guidelines for Safe Use
>> Assembly and Inspection
>> Movement Restrictions
>> Safety Equipment
● Additional Considerations for Mobile Tower Scaffold Use
>> Environmental and Site Conditions
>> Platform Size and Worker Movement
>> Training and Competency
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the maximum height for a mobile tower scaffold?
>> 2. Can mobile scaffolds be moved while workers are on them?
>> 3. What safety features should a mobile tower scaffold have?
>> 4. How do outriggers affect scaffold height?
>> 5. What environmental conditions affect mobile scaffold use?
Mobile tower scaffolds are essential tools in construction, maintenance, and various industrial applications where working at height is necessary. Knowing the maximum height for a mobile tower scaffold is critical to ensure safety, compliance with regulations, and operational efficiency. This comprehensive article explores the factors that determine the maximum height, relevant safety standards, practical guidelines, and answers common questions related to mobile tower scaffolds.

Understanding Mobile Tower Scaffolds
Mobile tower scaffolds, often referred to as mobile scaffolding or mobile work platforms, are prefabricated, movable structures designed to provide elevated workspaces. Unlike fixed scaffolds, mobile towers offer the advantage of mobility, allowing workers to reposition the scaffold easily without dismantling it.
What Defines a Mobile Tower Scaffold?
- Structure: Typically made of lightweight aluminum or steel components.
- Mobility: Equipped with lockable swivel castors or wheels for easy movement.
- Platform: A work platform at varying heights, usually with guardrails for safety.
- Access: Internal ladders or stairways to reach the platform safely.
Mobile scaffolds differ from mobile work platforms in regulatory terms. For example, in Europe, mobile work platforms are single-span constructions regulated by DIN EN 1004-1, while mobile scaffolds may consist of multiple spans and are regulated by DIN 4420-3.
Maximum Height Limits for Mobile Tower Scaffolds
International Standards and Regulations
The maximum height of a mobile tower scaffold varies depending on location, standards, and whether the scaffold is used indoors or outdoors.
| Region/Standard | Maximum Platform Height (Indoor) | Maximum Platform Height (Outdoor) |
| Europe (DIN EN 1004-1) | 12 meters (39.4 feet) | 8 meters (26.2 feet) |
| OSHA (USA) Height-to-Base Ratio | Based on 4:1 ratio (Height:Base Width) | Same |
| Australia/New Zealand (AS/NZS 1576) | 12 meters (39.4 feet) | Varies with conditions |
According to the MUNK Group, the maximum height for a mobile scaffold work platform is 12 meters indoors and 8 meters outdoors. Climbing up the outside of the scaffold to reach the platform is prohibited outdoors, and internal ladders must be part of the structure.
Height-to-Base Width Ratio
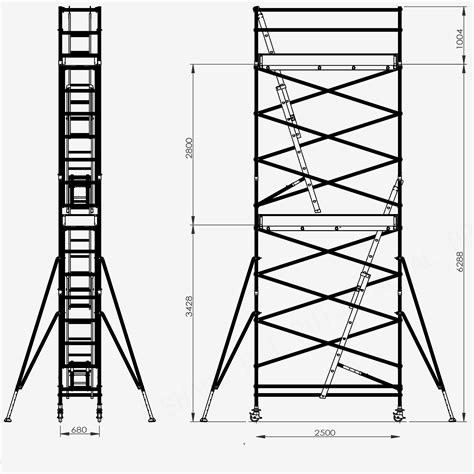
OSHA regulations specify a height-to-base width ratio of 4:1 for mobile scaffolds. This means the scaffold height should not exceed four times the narrowest base dimension to maintain stability. For example, a scaffold with a base width of 4 feet should not exceed 16 feet in height without additional stabilization measures.
When moving the scaffold with workers on it, OSHA requires a stricter 2:1 height-to-base ratio or that the scaffold meets nationally recognized stability tests (ANSI/SIA A92.5 and A92.6).
Additional Height Limitations
- The vertical distance between platforms should not exceed 2.25 meters (about 7.4 feet).
- The first platform should not be more than 3.40 meters (11.2 feet) above the ground.
- The scaffold should not be used as access or exit to other structures.
Factors Affecting Maximum Scaffold Height
1. Base Dimensions and Stability
The scaffold's base width is crucial for stability. Wider bases allow higher scaffolds without tipping risks. Outriggers can be added to increase the effective base width, permitting taller scaffold heights safely.
2. Use of Outriggers and Tie-ins
Outriggers extend the base footprint, enhancing stability and allowing for increased scaffold height. Tie-ins or guying the scaffold to a permanent structure also improve stability, enabling higher platforms.
3. Load Capacity and Duty Rating
Scaffolds have duty ratings based on load capacity:
- Light Duty: Up to 225 lbs (single user, light tools)
- Medium Duty: Up to 350 lbs (two users, moderate tools)
- Heavy Duty: Up to 500 lbs or more (multiple users, heavy equipment)
Exceeding load limits can compromise stability and safety.
4. Environmental Conditions
Wind, uneven ground, and weather can affect scaffold stability. Mobile towers should not be used in strong winds, and the surface must be firm and level.
Practical Guidelines for Safe Use
Assembly and Inspection
- Erect scaffolds on firm, level ground.
- Use internal ladders for safe access.
- Ensure platforms are fully boarded with guardrails and toe boards.
- Lock wheels when scaffold is in use.
- Conduct regular inspections for loose components or damage.
Movement Restrictions
- Do not move scaffolds with workers on them unless designed for such use and meeting OSHA stability requirements.
- Wheels must be locked when stationary.
- Avoid moving scaffolds on uneven or slippery surfaces.
Safety Equipment
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE) such as helmets and fall protection harnesses.
- Maintain clearance from overhead power lines and obstructions.
Additional Considerations for Mobile Tower Scaffold Use
Environmental and Site Conditions
Environmental factors can significantly impact the safe maximum height of mobile tower scaffolds. For instance, working outdoors exposes scaffolds to wind loads, which can destabilize the structure if it is too tall or not properly secured. It is recommended to avoid using mobile scaffolds in winds exceeding 28 mph (12.5 m/s). Additionally, rain or ice can make platforms slippery, increasing fall risk.
Uneven or soft ground can cause scaffolds to lean or collapse. Use base plates, adjustable legs, or mud sills to distribute the load evenly and maintain a level base. Always conduct a thorough site assessment before erecting a scaffold.
Platform Size and Worker Movement
The size of the working platform influences safety and productivity. Larger platforms provide more space for tools and materials, reducing the need for workers to move frequently or lean dangerously. However, larger platforms increase the scaffold's footprint, which may limit mobility in tight spaces.
Workers should avoid overreaching or leaning outside guardrails, as this can cause falls or tip the scaffold. Proper training on safe movement and positioning on the scaffold is essential.
Training and Competency
Only trained and competent personnel should erect, inspect, and use mobile tower scaffolds. Training should cover:
- Safe assembly and dismantling procedures.
- Understanding load limits and duty ratings.
- Recognizing hazards such as unstable ground or overhead obstructions.
- Proper use of fall protection equipment.
Regular refresher training ensures ongoing compliance and safety awareness.
Conclusion
The maximum height for a mobile tower scaffold depends on regulatory standards, scaffold design, base width, and environmental factors. Generally, indoors, the maximum platform height is about 12 meters (39.4 feet), while outdoors it is limited to 8 meters (26.2 feet) without additional stabilization. The height-to-base width ratio of 4:1 is a key safety guideline, with stricter limits when moving scaffolds with workers aboard. Proper assembly, use of outriggers, adherence to load limits, and compliance with safety regulations are essential to prevent accidents and ensure safe working at height. By considering environmental conditions, platform size, and ensuring proper training, workers can maximize safety and efficiency when using mobile tower scaffolds.
FAQ
1. What is the maximum height for a mobile tower scaffold?
The maximum platform height is typically 12 meters (39.4 feet) indoors and 8 meters (26.2 feet) outdoors, according to European standards. OSHA bases limits on a 4:1 height-to-base width ratio.
2. Can mobile scaffolds be moved while workers are on them?
Moving mobile scaffolds with workers on them is generally prohibited unless the scaffold meets stricter stability requirements and has a 2:1 height-to-base ratio or better.
3. What safety features should a mobile tower scaffold have?
Essential features include lockable wheels, guardrails, toe boards, internal ladders, and outriggers or tie-ins for taller scaffolds.
4. How do outriggers affect scaffold height?
Outriggers increase the effective base width, allowing for taller scaffold heights by improving stability.
5. What environmental conditions affect mobile scaffold use?
Strong winds, uneven or soft ground, and proximity to overhead power lines can limit scaffold height and safe use.






















