Content Menu
● Understanding Scaffolding Systems
>> Base Plates
>> Standards (Uprights)
>> Ledgers (Runners)
>> Transoms (Bearers)
>> Braces
>> Platforms (Boards)
>> Couplers
● Detailed Analysis of Stability Factors
>> Load Distribution
>> Ground Conditions
>> Weather Conditions
>> Design Compliance
>> Material Quality
>> Proper Assembly Techniques
● Best Practices for Scaffold Assembly
● Advanced Scaffolding Techniques
>> Tube and Coupler Scaffolding
>> System Scaffolding
>> Rolling Scaffolds
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the main components of a scaffolding system?
>> 2. How does proper load distribution affect scaffold stability?
>> 3. Why are braces important in a scaffolding system?
>> 4. What should be considered when preparing a foundation for scaffolding?
>> 5. How often should scaffolds be inspected?
● Citations:
Scaffolding systems are indispensable in construction, maintenance, and repair projects, providing safe and stable platforms for workers at height. The stability of these systems is paramount to ensuring worker safety and efficient project execution. Understanding how the various parts of a scaffolding system contribute to its overall stability is crucial for everyone involved in construction activities. This article delves into the roles, design considerations, and best practices for the assembly and usage of scaffolding components, offering a comprehensive guide to maintaining stability in scaffolding systems.
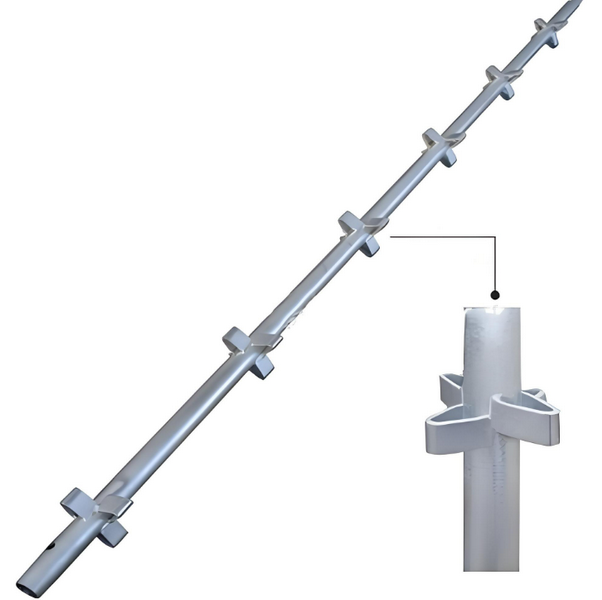
Understanding Scaffolding Systems
Scaffolding is a temporary structure that supports work platforms, materials, and workers during construction or maintenance. It comprises interconnected components designed to provide strength, stability, and safety. The primary parts of a scaffolding system include:
- Base Plates
- Standards (Uprights)
- Ledgers (Runners)
- Transoms (Bearers)
- Braces
- Platforms (Boards)
- Couplers
Base Plates
Base plates are the foundational elements of a scaffolding system, responsible for distributing the load of the scaffold evenly across the ground. They prevent the standards from sinking into soft soil, ensuring a stable footing for the entire structure. The proper installation of base plates is critical, particularly on uneven or unstable surfaces, where they provide a level starting point for the scaffolding system.
Standards (Uprights)
Standards are the vertical posts that bear the weight of the scaffold and transfer it to the base plates. Typically constructed from durable materials like galvanized steel or aluminum, standards must be robust enough to withstand significant vertical loads. The height and spacing of standards are critical design considerations that directly affect the load-bearing capacity and stability of the scaffolding system.
Ledgers (Runners)
Ledgers are horizontal members that connect the standards, providing lateral support and distributing loads across the structure. They are essential for maintaining the rigidity of the scaffolding system, preventing swaying, and enhancing overall strength. The placement and secure fastening of ledgers are vital for ensuring a stable and safe working environment.
Transoms (Bearers)
Transoms run perpendicular to the ledgers and provide additional support for the platforms. They ensure that the platforms remain stable under load and maintain the proper spacing and alignment of the standards. Transoms are crucial for creating a safe and reliable working surface, minimizing the risk of accidents.
Braces
Braces are diagonal components that reinforce the structural integrity of the scaffold. They prevent twisting and collapsing by providing additional support against lateral forces, such as wind or heavy loads. Cross-braces and façade braces are common types of braces, each serving specific purposes depending on the scaffold's design and environmental conditions.
Platforms (Boards)
Platforms form the working surface where construction activities take place. They are typically made from wooden planks or metal decks placed on ledgers and transoms. Safe platforms must be fully decked, securely fastened, and equipped with guardrails to protect workers from falls. The quality and proper installation of platforms are essential for ensuring worker safety and productivity.
Couplers
Couplers are connectors that securely fasten the various parts of scaffolding system together. They play a critical role in ensuring that all components are tightly interconnected, contributing to the overall stability and integrity of the scaffolding system. Different types of couplers are used to connect standards, ledgers, transoms, and braces, each designed to provide a strong and reliable connection.
Detailed Analysis of Stability Factors
The stability of a scaffolding system is influenced by a multitude of factors, each requiring careful consideration during the design, assembly, and usage phases.
Load Distribution
Proper load distribution is paramount to preventing overloading of any single component within the scaffolding system. Overloading can lead to structural failure and potential collapse. To ensure adequate load distribution, it is essential to calculate the maximum load the scaffold will bear, considering the weight of workers, materials, and equipment. Distributing the load evenly across the platform and avoiding concentrated loads in specific areas will enhance the stability of the structure.
Ground Conditions
The type of ground on which the scaffolding is erected significantly affects its stability. Soft or uneven surfaces can cause the base plates to sink, compromising the integrity of the entire system. Before erecting the scaffold, it is crucial to assess the ground conditions and take necessary measures to ensure a stable foundation. This may involve compacting the soil, using soleboards or mud sills to distribute the load, or employing adjustable base jacks to level the scaffold.
Weather Conditions
Weather conditions, particularly wind and rain, can significantly impact the stability of scaffolding systems. Wind exerts lateral forces on the scaffold, potentially causing it to sway or collapse. Rain can make the working surfaces slippery, increasing the risk of falls. To mitigate these risks, scaffolds should be designed to withstand anticipated wind loads, and additional bracing and securing methods should be employed during adverse weather conditions. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for any signs of instability caused by weather.
Design Compliance
Scaffolding systems must be designed by qualified professionals who understand structural engineering principles and safety regulations. The design should consider the specific requirements of the project, including the height and width of the scaffold, the anticipated loads, and the environmental conditions. Compliance with local regulations and standards is essential to ensure that the scaffolding system meets all safety requirements and is structurally sound.
Material Quality
The quality of materials used in the construction of scaffolding systems is critical for ensuring their stability and durability. High-quality steel or aluminum should be used for standards, ledgers, transoms, and braces to provide adequate strength and resistance to corrosion. Platforms should be made from durable materials that can withstand the anticipated loads and provide a safe working surface. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for any signs of wear, damage, or corrosion, and any compromised components should be replaced immediately.
Proper Assembly Techniques
The correct assembly of scaffolding components is essential for ensuring the stability and safety of the system. Workers assembling scaffolding should be properly trained in the correct techniques and procedures, following the manufacturer's instructions and safety guidelines. All connections should be securely fastened, and components should be properly aligned to ensure that loads are distributed evenly. Regular inspections should be conducted during the assembly process to verify that all components are correctly installed and that the scaffold is structurally sound.
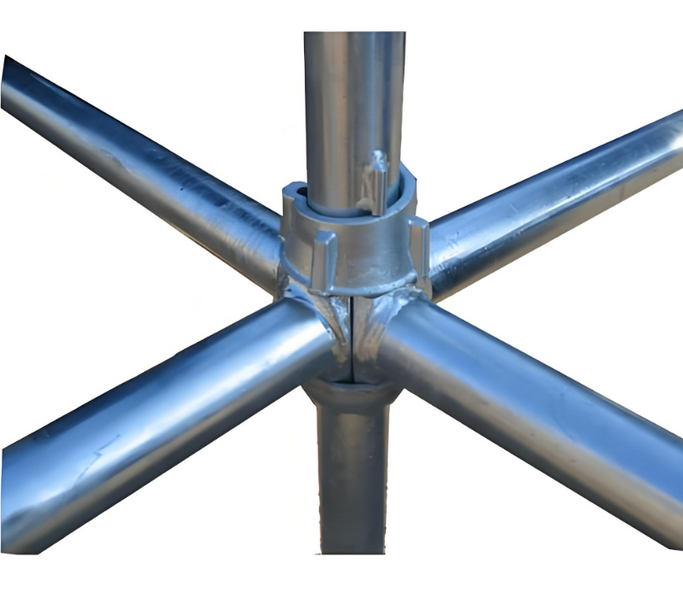
Best Practices for Scaffold Assembly
To ensure maximum stability and safety when assembling scaffolding systems, consider the following best practices:
1. Foundation Preparation: Ensure that the ground is stable, level, and capable of supporting the scaffold's weight. Use soleboards or mud sills on soft or uneven surfaces to distribute the load.
2. Use Quality Materials: Utilize high-quality materials for all components, including standards, ledgers, transoms, braces, platforms, and couplers. Ensure that all materials meet the required strength and durability standards.
3. Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections before, during, and after each use of the scaffold to identify any potential issues with stability, integrity, or safety. Inspect all components for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion, and replace any compromised components immediately.
4. Proper Training: Ensure that all personnel involved in erecting, dismantling, or using scaffolding are adequately trained in safety protocols and assembly techniques. Training should cover the correct procedures for assembling and disassembling the scaffold, inspecting components, and using fall protection equipment.
5. Adhere to Regulations: Follow local regulations and standards regarding scaffolding design, assembly, use, and dismantling. Ensure that the scaffold meets all safety requirements and that all necessary permits and approvals are obtained.
6. Use of Safety Equipment: All workers using scaffolding should be equipped with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including hard hats, safety glasses, and fall protection harnesses. Fall protection equipment should be properly inspected and used according to the manufacturer's instructions.
7. Secure Connections: Ensure that all connections between scaffolding components are securely fastened using appropriate couplers and fasteners. Regularly inspect connections to ensure they remain tight and secure.
8. Proper Bracing: Install braces according to the scaffold design to provide additional support and prevent swaying or collapse. Ensure that braces are properly aligned and securely fastened.
9. Load Limits: Adhere to the scaffold's load limits and avoid overloading the structure. Distribute loads evenly across the platform and avoid concentrated loads in specific areas.
10. Weather Precautions: Take appropriate precautions during adverse weather conditions, such as high winds or heavy rain. Secure the scaffold with additional bracing or tie-downs, and postpone work if conditions become too hazardous.
Advanced Scaffolding Techniques
Beyond the fundamental practices, several advanced techniques can further enhance the stability and safety of scaffolding systems.
Tube and Coupler Scaffolding
Tube and coupler scaffolding provides a highly versatile option where the parts of scaffolding system can be assembled in various configurations. This type of scaffolding requires skilled assemblers to ensure stability through correct alignment and secure coupling.
System Scaffolding
System scaffolding uses pre-engineered components that fit together in a modular fashion. This can speed up assembly and ensure a higher level of consistency and inherent stability, provided the system is used as designed.
Rolling Scaffolds
Rolling scaffolds (or mobile scaffolds) add wheels to the base of the scaffolding, allowing easy relocation. Stability is particularly crucial here, as movement adds dynamic forces. Ensure that the wheels are locked when in use and that the scaffold is only moved on level surfaces.
Conclusion
The various parts of scaffolding system each play crucial roles in ensuring its stability and safety during construction activities. By understanding the function of each component, adhering to best practices for assembly and use, and implementing advanced techniques where appropriate, workers can maintain a safe and productive working environment at heights. Regular inspections, proper training, and adherence to regulations are essential for preventing accidents and ensuring that scaffolding systems provide a reliable and secure platform for construction and maintenance activities.

FAQ
1. What are the main components of a scaffolding system?
The main components include base plates, standards (uprights), ledgers (runners), transoms (bearers), braces, platforms (boards), and couplers.
2. How does proper load distribution affect scaffold stability?
Proper load distribution prevents overloading any single component, which reduces the risk of structural failure and potential collapse. Distributing the load evenly across the platform is essential for stability.
3. Why are braces important in a scaffolding system?
Braces reinforce the structural integrity of the scaffold by preventing twisting and collapsing under lateral forces such as wind or heavy loads. They provide crucial diagonal support.
4. What should be considered when preparing a foundation for scaffolding?
Considerations include ground stability, levelness, and load-bearing capacity. On soft or uneven surfaces, use soleboards or mud sills to distribute the load. Adjustable base jacks can also be used to level the scaffold.
5. How often should scaffolds be inspected?
Scaffolds should be inspected regularly before each use, as well as after any event that could affect its stability, such as high winds or heavy rain. Regular inspections ensure that all components are secure and functioning properly.
Citations:
[1] https://www.discoscaff.co.za/scaffolding-components-fundamentals-of-scaffold-towers/
[2] https://www.safeworkaustralia.gov.au/system/files/documents/1703/scaffolds-scaffolding-work-general-guide.docx
[3] https://scaffoldtype.com/each-supported-scaffold-and-scaffolding-component/
[4] https://www.labour.gov.hk/eng/public/os/B/mss.pdf
[5] https://www.hsestudyguide.com/components-of-scaffolding/
[6] https://www.ihsa.ca/rtf/health_safety_manual/pdfs/equipment/Scaffolds.pdf
[7] https://www.avontus.com/scaffolding-encyclopedia/seven-fundamental-parts-of-a-scaffold/
[8] https://cn.linguee.com/%E8%8B%B1%E8%AF%AD-%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87/%E7%BF%BB%E8%AD%AF/scaffold+construction.html
[9] https://www.scaffoldingsolutions.com/articles/why-system-scaffolding-is-the-safest-scaffolding/






















