Content Menu
● Understanding Main Frame Scaffolding
● Step-by-Step Guide: How to Assemble Main Frame Scaffolding
>> 1. Preparation and Planning
>> 2. Laying the Foundation
>> 3. Assembling the First Level
>> 4. Building Additional Levels
>> 5. Installing Guardrails and Toe Boards
>> 6. Final Inspection and Safety Checks
● Best Practices for Main Frame Scaffolding Assembly
● Common Mistakes to Avoid
● Maintenance and Inspection During Use
● Expanding Main Frame Scaffolding for Complex Projects
● Main Frame Scaffolding Safety Enhancements
>> 1. Integrated Access Solutions
>> 2. Advanced Guardrail Systems
>> 3. Debris Netting and Enclosures
● Case Study: Main Frame Scaffolding for a Commercial Building
● Innovations in Main Frame Scaffolding Assembly
● Environmental and Safety Considerations
● Tips for Efficient Main Frame Scaffolding Assembly
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the essential components required for main frame scaffolding assembly?
>> 2. How do you ensure main frame scaffolding is stable and level?
>> 3. What safety features must be installed on main frame scaffolding?
>> 4. How often should main frame scaffolding be inspected?
>> 5. Can main frame scaffolding be used on uneven ground?
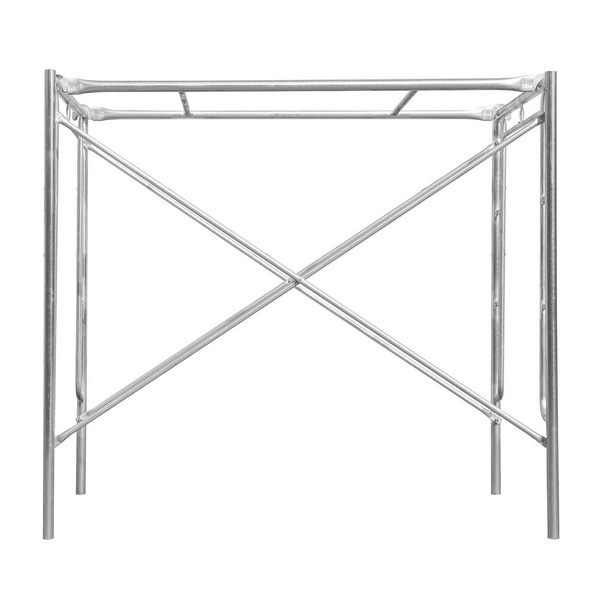
Main frame scaffolding, also known as frame scaffolding or H frame scaffolding, is one of the most widely used scaffolding systems in construction due to its simplicity, versatility, and efficiency. Proper assembly is crucial for the safety of workers and the success of any project. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed, step-by-step explanation of how main frame scaffolding is assembled on site.
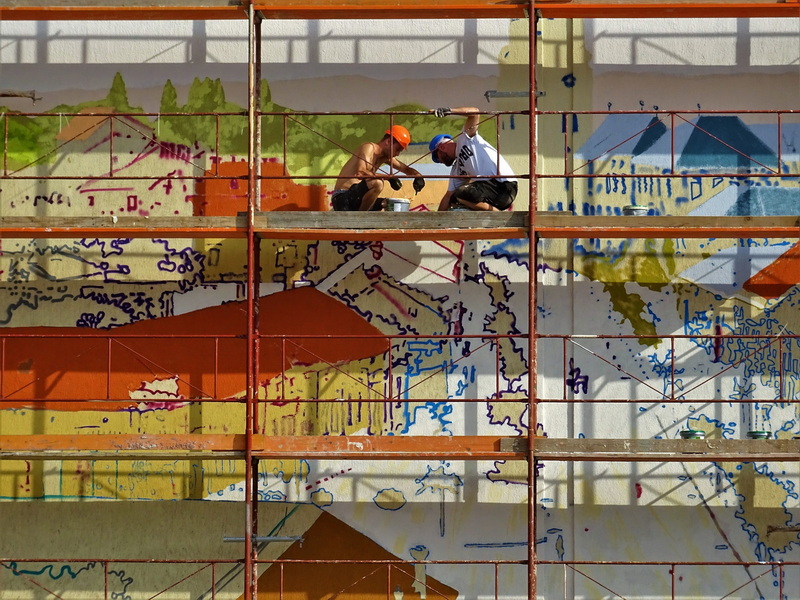

Understanding Main Frame Scaffolding
Main frame scaffolding is composed of vertical frames (often shaped like an “H”), cross braces, platforms, base plates or wheels, guardrails, and various locking mechanisms. Its modular design allows for rapid assembly and disassembly, making it ideal for both small and large construction projects.
Key Components:
- Main Frames (H-Frames): The vertical backbone of the scaffold.
- Cross Braces: Provide lateral stability.
- Horizontal Braces/Ledgers: Add rigidity and support platforms.
- Platforms/Planks: The working surface for personnel and materials.
- Base Plates/Adjustable Jacks: Ensure a stable and level foundation.
- Guardrails and Toe Boards: Essential for fall protection.
- Coupling Pins and Locks: Secure frames and braces together.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Assemble Main Frame Scaffolding
1. Preparation and Planning
Before starting assembly, careful preparation is vital:
- Inspect All Components: Check for damage, wear, or defects. Do not use bent, rusted, or cracked parts.
- Clear the Area: Remove debris, mud, and obstructions from the ground.
- Assess Ground Conditions: Ensure the ground is level, solid, and free from holes or soft spots. Use mud sills or timber bases on soft ground.
- Gather Tools and Safety Gear: Have all required components and personal protective equipment (PPE) ready.
2. Laying the Foundation
A stable base is the cornerstone of safe scaffolding:
- Place Base Plates or Adjustable Jacks: Position them according to the desired scaffold footprint.
- Level the Base: Use a spirit level to ensure all base plates are even. Adjust jacks as necessary.
- Secure on Soft Ground: If on soil, use mud sills or timber planks under base plates to distribute weight.
3. Assembling the First Level
- Install the First Set of Main Frames: Place two main frames upright on the base plates.
- Attach Cross Braces: Connect the frames using cross braces. Secure each end with the locking mechanism (J-lock, C-lock, etc.).
- Check for Plumb and Level: Use a spirit level to ensure the frames are vertically plumb and horizontally level. Adjust as needed.
- Install Platforms/Planks: Place the working platform or planks onto the horizontal ledgers or frame supports. Secure them to prevent movement.
4. Building Additional Levels
- Stack Additional Frames: Insert coupling pins into the top of the first level frames, then stack the next set of frames on top.
- Secure with Cross Braces: Repeat the process of attaching cross braces and checking for plumb and level after each level.
- Install Platforms: Add platforms at each working level as required.
- Tie Scaffold to Structure: For heights above 4 times the minimum base width, tie the scaffold to the building at regular intervals (typically every 30 feet horizontally and every 4 times the base width vertically).
5. Installing Guardrails and Toe Boards
- Guardrails: Attach guardrail posts to the top of each frame. Secure guardrails on all open sides at each working level.
- Toe Boards: Install toe boards along the edges of platforms to prevent tools and materials from falling.
- Access Ladders/Stairs: Provide safe access to each level with ladders or stairways integrated into the scaffold.
6. Final Inspection and Safety Checks
- Double-Check All Connections: Ensure all braces, pins, and locks are secure and properly engaged.
- Verify Stability: Confirm the scaffold is stable, plumb, and level at all points.
- Inspect Platforms: Ensure all platforms are fully decked, secured, and free from defects.
- Check Ties and Bracing: Ensure all ties to the structure and diagonal bracing are installed as required.
- Install Safety Netting: If needed, install safety netting or debris mesh on the exterior of the scaffold.
Best Practices for Main Frame Scaffolding Assembly
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always adhere to the manufacturer's assembly instructions and weight limits.
- Conduct Regular Inspections: Inspect the scaffold before use and periodically during the project for any signs of damage or instability.
- Provide Adequate Training: Ensure all workers are trained in scaffold assembly, use, and emergency procedures.
- Implement Fall Protection: Use guardrails, toe boards, and personal fall arrest systems where required.
- Maintain a Clean Work Area: Keep the area around the scaffold clear of debris and obstacles to prevent tripping hazards.
- Never Exceed Load Limits: Always be aware of the scaffold's rated capacity and do not overload platforms with workers, tools, or materials.

Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping Level Checks: Failing to ensure the scaffold is plumb and level can result in instability and collapse.
- Improper Bracing: Missing or improperly installed cross braces can compromise structural integrity.
- Inadequate Tying: Not tying the scaffold to the structure at required intervals increases the risk of tipping.
- Using Damaged Components: Always replace bent, cracked, or rusted parts before assembly.
- Ignoring Manufacturer Instructions: Each main frame scaffolding system may have specific requirements-always consult the manual.
Maintenance and Inspection During Use
- Daily Visual Checks: Look for loose connections, missing pins, or signs of wear.
- Weekly Detailed Inspections: Check all braces, platforms, and ties for security.
- After Severe Weather: Inspect for movement, water damage, or instability.
- Cleaning: Remove mud, debris, and materials from platforms and around the base.
Expanding Main Frame Scaffolding for Complex Projects
Main frame scaffolding is not limited to simple, straight runs. For larger or more complex projects, the system can be expanded and adapted:
- Bridging Bays: Use bridging ledgers or trusses to span openings such as doorways or driveways.
- Corner Assemblies: Specialized corner frames or clamps allow scaffolding to wrap around building corners, providing continuous access.
- Cantilevered Platforms: For areas where ground access is restricted, cantilever brackets can extend platforms beyond the main structure.
- Mobile Towers: By adding caster wheels, main frame scaffolding can be converted into mobile towers for interior work or frequent repositioning.
Main Frame Scaffolding Safety Enhancements
1. Integrated Access Solutions
Modern main frame scaffolding often includes built-in ladders or stair towers, providing safer and more convenient access to each level compared to traditional portable ladders.
2. Advanced Guardrail Systems
Some systems feature snap-on or tool-free guardrails, reducing assembly time and ensuring consistent safety compliance.
3. Debris Netting and Enclosures
For projects in urban environments or where falling debris is a concern, debris netting or full scaffold enclosures can be installed to protect workers and the public.
Case Study: Main Frame Scaffolding for a Commercial Building
A construction team needed to install exterior cladding on a five-story office building. They chose main frame scaffolding for its speed and modularity. The assembly process included:
- Using adjustable jacks and mud sills for a stable base on uneven ground.
- Stacking frames to reach each floor, with platforms installed at every level.
- Tying the scaffold to the building at every floor for maximum stability.
- Installing guardrails and toe boards on all working platforms.
- Conducting daily inspections and weekly safety meetings.
The project was completed safely and efficiently, with no incidents-demonstrating the effectiveness of following best practices for main frame scaffolding assembly.
Innovations in Main Frame Scaffolding Assembly
- Quick-Lock Mechanisms: Modern systems use tool-free locking pins for faster, safer assembly.
- Integrated Ladders and Stairs: Built-in access solutions improve safety and speed.
- Lightweight Materials: High-strength aluminum and advanced coatings reduce weight and corrosion.
- Digital Inspection Tags: RFID or QR code tags for tracking inspections and maintenance.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Reusable Components: Main frame scaffolding is designed for repeated use, reducing waste.
- Recyclable Materials: Most frames are made from steel or aluminum, both recyclable.
- Safety Compliance: Always follow OSHA, local, and manufacturer safety standards to protect workers and the public.
Tips for Efficient Main Frame Scaffolding Assembly
1. Organize Components by Level: Lay out all frames, braces, and platforms for each level before starting assembly.
2. Work in Teams: Assembly is faster and safer with at least two people.
3. Use Color Coding: Some systems use color-coded braces or pins for easier identification and assembly.
4. Keep Documentation Handy: Always have the manufacturer's assembly manual on site for reference.
5. Plan for Dismantling: Assemble with dismantling in mind, keeping access clear for safe removal at project completion.
Conclusion
Main frame scaffolding is a proven, efficient, and safe solution for supporting workers and materials on construction sites. Proper assembly is critical: start with a stable base, build level by level with secure bracing and platforms, install guardrails and toe boards, and always tie the scaffold to the structure for stability. Follow manufacturer guidelines, conduct regular inspections, and train all personnel in safe assembly and use. By adhering to these principles, main frame scaffolding can be assembled quickly and safely, supporting successful project outcomes.
FAQ
1. What are the essential components required for main frame scaffolding assembly?
Main frame scaffolding requires vertical frames (H-frames), cross braces, platforms or planks, base plates or adjustable jacks, guardrails, toe boards, coupling pins, and locking mechanisms.
2. How do you ensure main frame scaffolding is stable and level?
Always use base plates or adjustable jacks on a solid, level foundation. Use a spirit level during assembly and adjust as needed. Secure all braces and tie the scaffold to the structure at required intervals.
3. What safety features must be installed on main frame scaffolding?
Install guardrails and toe boards on all working platforms, provide safe access with ladders or stairs, and use personal fall arrest systems where required by regulations.
4. How often should main frame scaffolding be inspected?
Inspect all components before assembly, daily during use, and after severe weather or impact. Conduct weekly detailed inspections for structural integrity.
5. Can main frame scaffolding be used on uneven ground?
Yes, but always use adjustable jacks and mud sills to level the base and ensure stability. Never assemble scaffolding on unstable or soft ground without proper support.






















