Content Menu
● Introduction to Frame Conventional Scaffolding
● Components of Frame Conventional Scaffolding
● Step-by-Step Installation Guide
>> Step 1: Prepare the Ground
>> Step 2: Assemble the First Frame
>> Step 3: Add Additional Frames and Bracing
>> Step 4: Install Platforms and Safety Features
>> Step 5: Final Inspection and Use
● Safety Tips for Using Frame Conventional Scaffolding
>> Safety Dos
>> Safety Don'ts
● Common Hazards and Solutions
>> Hazards
>> Solutions
● Advanced Safety Measures
>> Use of Safety Nets
>> Fall Protection Equipment
>> Regular Training Sessions
● Compliance with Regulations
● Key Regulations
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the key components of a frame conventional scaffolding?
>> 2. How often should scaffolding be inspected?
>> 3. What safety equipment is essential for scaffolding work?
>> 4. Can scaffolding be used in adverse weather conditions?
>> 5. What is the recommended load capacity for scaffolding?
● Citations:
Safely installing and using a frame conventional scaffolding is crucial for ensuring the safety of workers and the success of construction projects. This type of scaffolding is widely used due to its versatility and ease of assembly. In this article, we will guide you through the steps of setting up and using a frame conventional scaffolding safely, highlighting key safety tips and best practices.
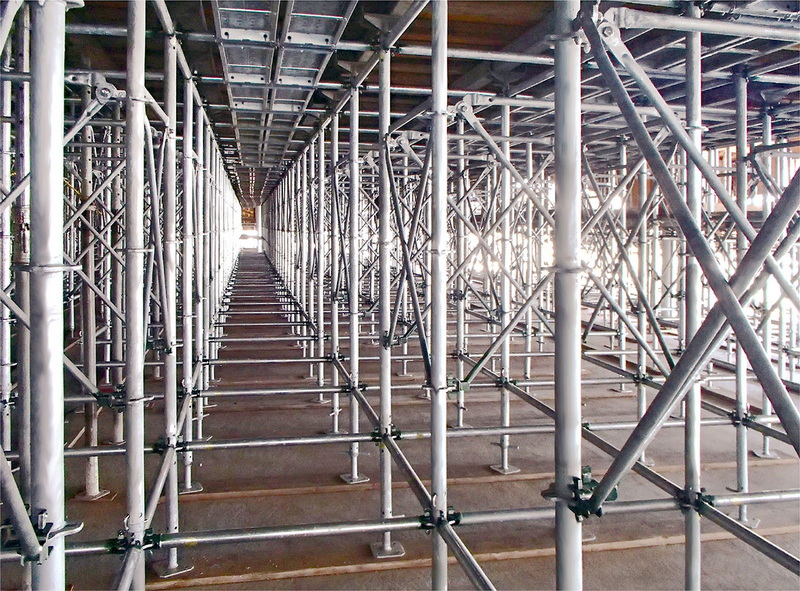

Introduction to Frame Conventional Scaffolding
Frame conventional scaffolding consists of prefabricated frames that are connected by horizontal and diagonal bracing to form a stable structure. It is commonly used in construction, maintenance, and repair projects due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
Components of Frame Conventional Scaffolding
- Frames: These are the main vertical components of the scaffolding. They come in various heights, typically 2 meters (6 feet 6 inches) for standard use.
- Horizontal Bracing: These are used to connect frames and provide additional stability.
- Diagonal Bracing: Essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the scaffolding by forming a cross pattern.
- Platforms: These are the working surfaces where workers stand and perform tasks.
- Guardrails and Toeboards: Safety features to prevent falls and protect workers.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Step 1: Prepare the Ground
Ensure the ground is level and firm. Use sills or base plates to distribute the weight evenly. Replace soft soil with gravel or crushed stone if necessary. This step is critical to prevent the scaffolding from shifting or collapsing.
Step 2: Assemble the First Frame
1. Place the first frame on the base plates.
2. Connect the first cross brace to secure the frame.
3. Ensure the frame is plumb and level. Use a spirit level to verify this.
Step 3: Add Additional Frames and Bracing
1. Install the second frame and connect it with the first frame using cross braces.
2. Add diagonal bracing to maintain stability and form a cross pattern. This pattern helps distribute the load evenly across the structure.
Step 4: Install Platforms and Safety Features
1. Place platforms on the frames, ensuring they are securely fastened with platform clips.
2. Install guardrails and toeboards on all exposed sides. These are crucial for preventing falls and protecting workers from falling objects.
Step 5: Final Inspection and Use
- Conduct a thorough inspection to ensure all components are securely in place. Use a checklist to verify each step.
- Use safety equipment such as harnesses and lanyards when working at heights. Ensure all workers are trained on the proper use of this equipment.
Safety Tips for Using Frame Conventional Scaffolding
Safety Dos
- Inspect Before Use: Always inspect the scaffolding before each shift using a checklist or mobile app. This helps identify any potential hazards.
- Proper Training: Ensure all workers are trained on scaffolding safety and assembly. This includes understanding load capacities and safety equipment use.
- Use PPE: Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as hard hats and non-slip shoes. This protects workers from falling objects and slips.
- Load Capacity: Be aware of the scaffold's load capacity to prevent overloading. This includes the weight of workers, tools, and materials.
- Weather Conditions: Avoid using scaffolding during adverse weather conditions such as strong winds or heavy rain. These conditions can destabilize the scaffolding.
Safety Don'ts
- Don't Overload: Never exceed the recommended load capacity. Overloading can lead to structural failure.
- Don't Use Damaged Equipment: Inspect for damage before use and avoid using damaged scaffolding components. Damaged parts can compromise the structure's integrity.
- Don't Lean Over: Always stay within the guardrails and avoid leaning over the sides. This reduces the risk of falls.
Common Hazards and Solutions
Hazards
- Structural Failure: Caused by improper assembly or overloading. This can lead to catastrophic collapses.
- Falls: Resulting from inadequate guardrails or misuse of safety equipment. Falls are a leading cause of injury on construction sites.
- Collisions: From falling objects or tools. These can cause serious injury or death.
Solutions
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain scaffolding components. This includes checking for rust or damage.
- Proper Assembly: Follow manufacturer instructions for assembly. Ensure all parts are securely connected.
- Safety Nets: Use safety nets to catch falling objects. These can be installed below the scaffolding to protect workers and bystanders.
Advanced Safety Measures
Use of Safety Nets
Safety nets are an effective way to protect workers from falling objects. They should be installed below the scaffolding and checked regularly for damage.
Fall Protection Equipment
Fall protection equipment such as harnesses and lanyards should be used by all workers when working at heights. Ensure that these are properly fitted and inspected before use.
Regular Training Sessions
Conduct regular training sessions for workers on scaffolding safety and assembly. This includes understanding load capacities, recognizing hazards, and using safety equipment correctly.
Compliance with Regulations
Ensure that all scaffolding installations comply with local and national safety regulations. This includes adhering to standards for assembly, inspection, and use.
Key Regulations
- OSHA Standards: In the U.S., OSHA provides guidelines for scaffolding safety, including requirements for assembly, inspection, and fall protection.
- EU Safety Directives: In Europe, directives outline specific safety standards for scaffolding, including training requirements and equipment specifications.
Conclusion
Installing and using a frame conventional scaffolding safely requires careful planning, proper assembly, and adherence to safety guidelines. By following these steps and tips, you can minimize risks and ensure a successful project. Always prioritize worker safety and comply with local regulations.

FAQ
1. What are the key components of a frame conventional scaffolding?
The key components include frames, horizontal and diagonal bracing, platforms, guardrails, and toeboards.
2. How often should scaffolding be inspected?
Scaffolding should be inspected before each work shift using a checklist or mobile inspection app.
3. What safety equipment is essential for scaffolding work?
Essential safety equipment includes hard hats, non-slip shoes, safety belts, and lanyards for heights over 10 feet.
4. Can scaffolding be used in adverse weather conditions?
No, scaffolding should not be used during adverse weather conditions such as strong winds or heavy rain.
5. What is the recommended load capacity for scaffolding?
Scaffolding should be designed to support four times the maximum intended load without failure.
Citations:
[1] https://www.datocms-assets.com/48781/1626165723-mounting-instruction-scaffolds-st-rt-fteng.pdf
[2] https://scsaonline.ca/pdf/Frame_Scaffold_Safety_Aug_2018.pdf
[3] https://safetyculture.com/topics/scaffolding-safety/
[4] https://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/safety_haz/platforms/components.html
[5] https://www.metaltech.co/setup-instructions/
[6] https://yorkscaffold.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/code-safe-practices-frames.pdf
[7] https://www.tdi.texas.gov/tips/safety/scaffolding.html
[8] https://www.safework.nsw.gov.au/resource-library/scaffolding/erecting,-altering-and-dismantling-scaffolding-part-1-prefabricated-steel-modular-scaffolding
[9] https://brandsafway.com/uploads/files/orn703_bsl_safmax_assembly_instructions.pdf
[10] https://www.saiaonline.org/files/COSP%20for%20Frame,%20System,%20Tube%20and%20Clamp,%20and%20Rolling%20Scaffolds.pdf
[11] https://www.safeworkaustralia.gov.au/system/files/documents/1703/guide-scaffolds-scaffolding.pdf






















