Content Menu
● Introduction to Aluminum Scaffolding Parts
● Common Aluminum Scaffolding Parts and Their Names
>> 1. Standards (Vertical Supports)
>> 2. Ledgers (Horizontal Tubes)
>> 3. Transoms (Cross Tubes)
>> 4. Base Plates
>> 5. Sole Boards
>> 6. Braces (Diagonal Tubes)
>> 7. Couplers (Clamps)
>> 8. Boards / Platforms
>> 9. Guardrails (Handrails and Midrails)
>> 10. Toe Boards
>> 11. Wheels / Castors
>> 12. Ladders
>> 13. Ties
>> 14. Stage Toppers
>> 15. Hop-Ups
● Safety Standards and Regulations for Aluminum Scaffolding Parts
>> Load Capacity and Structural Integrity
>> Guardrails and Fall Protection
>> Stability and Bracing
>> Inspection and Maintenance
● Assembly and Maintenance Tips for Aluminum Scaffolding Parts
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the main vertical supports in aluminum scaffolding called?
>> 2. Which parts provide horizontal support in scaffolding?
>> 3. What is the purpose of base plates in scaffolding?
>> 4. How do guardrails and toe boards contribute to safety?
>> 5. What role do couplers play in aluminum scaffolding?
Aluminum scaffolding is a crucial component in construction, maintenance, and repair projects, providing workers with safe and stable elevated platforms. Understanding the aluminum scaffolding parts name and their functions is essential for proper assembly, safety, and efficient use. This comprehensive guide explores the common parts of aluminum scaffolding, their roles, and how they come together to form a reliable structure.
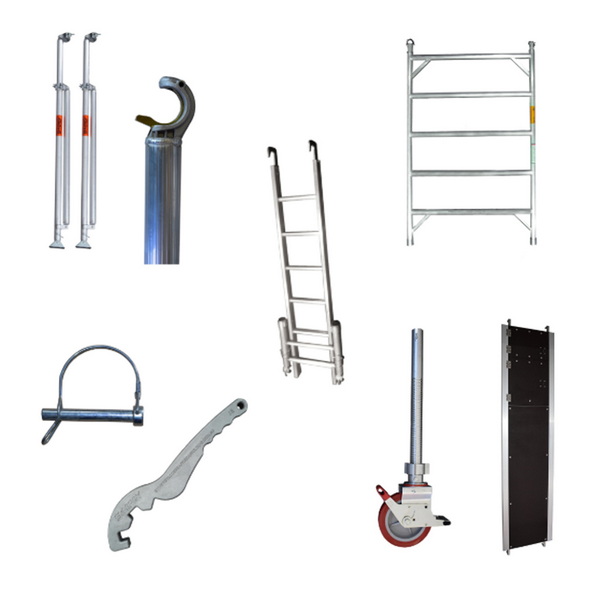

Introduction to Aluminum Scaffolding Parts
Aluminum scaffolding systems consist of multiple components that interlock and support each other to create a temporary, elevated work platform. These parts are designed to be lightweight, durable, and easy to assemble. Knowing the aluminum scaffolding parts name helps workers, supervisors, and DIY enthusiasts identify each element and ensure correct usage.
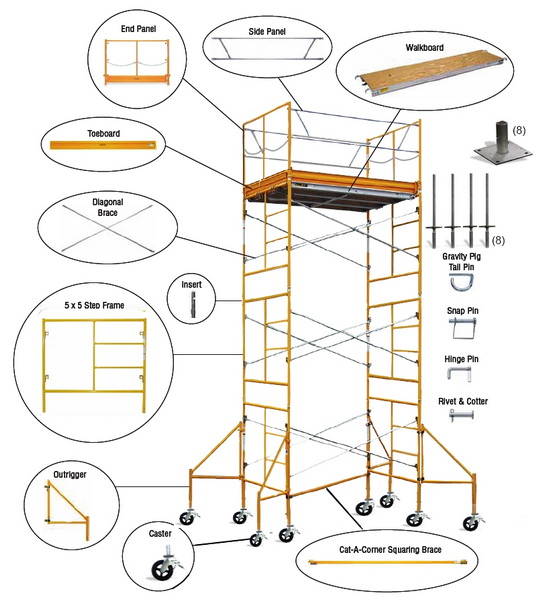
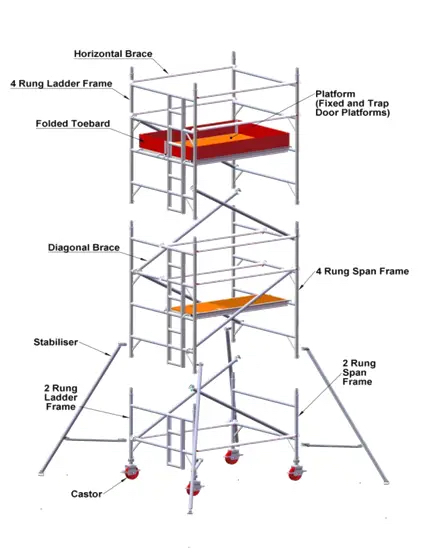
Common Aluminum Scaffolding Parts and Their Names
1. Standards (Vertical Supports)
Standards are the vertical tubes or poles that form the main framework of the scaffolding. They transfer the entire weight of the scaffold and the workers to the ground or foundation. Standards are connected to the base plates at the bottom to distribute the load evenly.
- Function: Provide vertical support and stability.
- Details: Usually come in various lengths and are staggered for height extension.
2. Ledgers (Horizontal Tubes)
Ledgers are horizontal tubes that run parallel to the building facade and connect the standards. They provide lateral support and help distribute the load evenly across the structure.
- Function: Support transoms and platforms; maintain scaffold rigidity.
- Details: Non-load bearing in some systems but essential for structural integrity.
3. Transoms (Cross Tubes)
Transoms run perpendicular to the ledgers and hold the working platforms or boards. They help stabilize the scaffold by connecting opposite ledgers.
- Function: Support platforms and improve scaffold stability.
- Details: Main transoms support the working platform; intermediate transoms may be used for additional support.
4. Base Plates
Base plates are flat plates attached to the bottom of standards. They distribute the weight of the scaffold to the ground and prevent the standards from sinking into soft surfaces.
- Function: Provide a stable foundation and distribute load.
- Details: Often used with sole boards on soft ground for extra support.
5. Sole Boards
Sole boards are wooden or metal planks placed under base plates to spread the load over a larger area, especially on soft or uneven ground.
- Function: Prevent sinking and increase stability.
6. Braces (Diagonal Tubes)
Braces are diagonal tubes that connect standards and ledgers to increase the rigidity and prevent swaying.
- Function: Enhance structural strength and prevent lateral movement.
- Details: Can be cross braces or diagonal braces.
7. Couplers (Clamps)
Couplers are clamps used to connect different scaffolding parts, such as standards to ledgers or braces.
- Function: Securely join scaffolding components.
- Types: Right-angle couplers, swivel couplers, sleeve couplers.
8. Boards / Platforms
Boards or platforms are the working surfaces where workers stand and place tools or materials.
- Function: Provide safe and stable working areas.
- Materials: Aluminum planks, timber planks, or steel decks.
9. Guardrails (Handrails and Midrails)
Guardrails are horizontal rails installed at the edges of platforms to prevent falls.
- Function: Enhance worker safety by preventing falls.
- Details: Usually include a top rail and a mid-rail.
10. Toe Boards
Toe boards are vertical barriers at the platform edges to prevent tools or materials from falling off.
- Function: Prevent objects from falling and causing injuries below.
- Height: Typically at least 6 inches tall.
11. Wheels / Castors
Wheels or castors are attached to the base of mobile scaffolding towers to allow easy movement.
- Function: Provide mobility.
- Features: Include locking mechanisms to secure the scaffold in place during use.
12. Ladders
Ladders are integrated or attached to scaffolding to provide safe access to different platform levels.
- Function: Safe vertical access.
- Types: Vertical ladders, stair ladders, inclined ladders.
13. Ties
Ties secure the scaffold to the building or structure to prevent tipping or swaying.
- Function: Stabilize the scaffold by anchoring it to a solid structure.
14. Stage Toppers
Stage toppers are additional frames placed on top of scaffolding to increase height safely.
- Function: Extend working height while maintaining structural integrity.
15. Hop-Ups
Hop-ups are small platforms or brackets that extend the working area beyond the scaffold frame.
- Function: Provide extra working space or reach in tight areas.
Safety Standards and Regulations for Aluminum Scaffolding Parts
Understanding the aluminum scaffolding parts name is only part of the equation; knowing how to use them safely is equally critical. Regulatory bodies such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute) provide comprehensive safety standards to ensure scaffolding is safe for workers.
Load Capacity and Structural Integrity
According to OSHA, all scaffolding components and the assembled structure must support at least four times the maximum intended load without failure. This includes the weight of workers, tools, and materials. For example, if the maximum load is 1,000 pounds, the scaffold must be capable of supporting at least 4,000 pounds.
Guardrails and Fall Protection
Guardrails, including toprails and midrails, must be installed on all open sides of scaffolds more than 10 feet above a lower level. The toprail height must be between 38 and 45 inches, depending on when the scaffold was manufactured. Toe boards of at least 4 inches in height are also required to prevent falling objects.
Stability and Bracing
Scaffolds with a height-to-base ratio greater than 4:1 must be secured with ties, braces, or outriggers to prevent tipping. All braces and couplers must be installed according to manufacturer specifications and inspected regularly for damage or wear.
Inspection and Maintenance
Regular inspections are mandatory before each use to check for damaged or missing parts, corrosion, and proper assembly. Damaged components should be replaced immediately to maintain safety.
Assembly and Maintenance Tips for Aluminum Scaffolding Parts
Proper assembly and maintenance of scaffolding parts are essential for safety and longevity.
- Start with a Level Base: Use base plates and sole boards to create a stable foundation.
- Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Use the correct couplers and braces as specified.
- Install Guardrails and Toe Boards: Always install fall protection systems before use.
- Lock Wheels: For mobile scaffolds, ensure wheels are locked before climbing.
- Regular Cleaning: Remove dirt, paint, and debris after each use to prevent corrosion.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Keep couplers and wheels functioning smoothly.
- Store Properly: Store scaffolding parts in dry, covered areas to prevent weather damage.
Conclusion
The aluminum scaffolding system is a complex assembly of various parts, each serving a vital role in ensuring safety, stability, and functionality. From the vertical standards to the horizontal ledgers and transoms, and from the base plates to the guardrails and toe boards, every component must be correctly identified and used. Familiarity with the aluminum scaffolding parts name helps workers and supervisors build and maintain scaffolds safely and efficiently. With the rise of modular and mobile scaffolding systems, understanding these parts becomes even more important to adapt to modern construction needs. Adhering to safety standards and proper maintenance ensures scaffolding remains a reliable and safe tool on any job site.
FAQ
1. What are the main vertical supports in aluminum scaffolding called?
They are called standards, and they transfer the load from the scaffold to the ground.
2. Which parts provide horizontal support in scaffolding?
Ledgers run parallel to the building, and transoms run perpendicular, supporting platforms.
3. What is the purpose of base plates in scaffolding?
Base plates distribute the load from standards to the ground and provide a stable foundation.
4. How do guardrails and toe boards contribute to safety?
Guardrails prevent workers from falling off platforms, while toe boards stop tools and materials from falling.
5. What role do couplers play in aluminum scaffolding?
Couplers are clamps that connect different scaffolding parts securely.






















